| ImmunCR Id : | ICR38 |
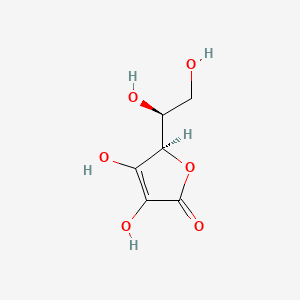
| Chemical Name : | Ascorbic acid |
| Plant Source : | Musa |
| Nutraceutical information : | Edible, widely found in citrus fruits, strawberries, tomatoes, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, green peppers, red peppers, turnips, and other leafy vegetables, small amounts in milk and fish. |
| Mode of administration : | Oral, intravenous |
| Immunomodulatory mechanism : | Antioxidant (reducing unstable free radicals of oxygen, nitrogen, and sulphur and also by enhancing the activity of another antioxidant, tocopherol (vitamin E); oxidized into a fairly unreactive ascorbate radical, which through NADH/NADPH-dependent reductases is converted back to ascorbate; in association with vitamin E synergistically functions as a co-antioxidant to shield LDL from ROS ),attenuates inflammatory response, including sepsis syndrome, anti-cancer (generates H2O2 in cancer cells through organometallic reaction and causes selective cytotoxicity to cancer cells; at high concentration curbed cell migration and capillary-like tube formation; acts as a co-factor to the phds (prolyl hydroxylase domain enzymes) to recycle and maintain ferrous ion (Fe2+), Therefore, the presence of ascorbate can impact HIF(Hypoxia-inducible factors) function, which in turn can affect tumour progression; reduces DNA damage and mutations through degradation of HIF-1α levels by enhancing the action of HIF hydroxylases; intravenous high concentrations of ascorbic acid selectively interfere with mutated KRAS or BRAF, inducing GLUT1 regulation of glycolysis and killing cancer cells; acts as a cofacator for TET1, TET2, and TET3 proteins); formation of collagen, wound healing, repair of body tissues, and nurturing of bones, cartilage, and teeth; Proline residues on procollagen require vitamin C for hydroxylation, making it necessary for the triple-helix formation of mature collagen. |
| Description : | Two transporters are involved: svcts (sodium-dependent vitamin C transporters) and hexose transporters. The site for absorption is the distal small intestine and is regulated by renal excretion. The highest ascorbic acid concentrations are in the pituitary gland, the adrenal gland, the brain, leukocytes, and the eyes. |
| IUPAC Name | (2R)-2-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-3,4-dihydroxy-2H-furan-5-one |
| SMILES | C([C@@H]([C@@H]1C(=C(C(=O)O1)O)O)O)O |
| Formula | C6H8O6 |
| InchiKey | CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N |
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Superclass | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
| Class | Dihydrofurans |
| Subclass | Furanones |
| LogP | -1.709 |
| Molecular weight | 176.124 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 4 |
| Polar surface area | 109.492 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 2 |
| Number of Aromatic Rings | 0 |
| Number of rings | 1 |
| Absorption level | Moderate |
| Solubility level | Very Soluble |
| Blood Brain Barrier | Undefined |
| Plasma protein binding | Non-Binder |
| CYP2D6 inhibition | Non-Inhibitor |