| Immunomodulatory mechanism :
|
Antioxidant (inhibits lipid peroxidation, 2-deoxyribose, upregulates superoxide radical scavenging); Anti-inflammatory (upregulates TNF-α, NO, downregulates NF-kb, JAK-STAT1/3 pathway) Anti-Alzheimer (inhibits ache, 5-LOX enzyme); Brain ischemia (upregulates SOD, GSH, IL-10, downregulates malondialdehyde, IL-1β, TNF-α); Hepatoprotective (activates Nrf2, inhibits NLRP3 activation); Anti-Diabetic (inhibits protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, isomaltase, glucoside anzyme, sucrase, maltase); Anti-cancer (inhibits COX-2, VEGF-A, phosphorylation of (mapks 38, ERK (Extracellular signal-Regulated kinase), JNK), upregulates pparү mrna expression, TGF-β, igm, igg, cytochrome C release, FADD (FAS associated Death Domain), Bax, caspase-3,-6,-8,-9, PARP (poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase), G2/M phase cell cycle arrest, downregulates iga, β-catenin pathway, MMP-7, MMP-9, Bcl-2, XIAP, Bcl-xl)
|
| Description : |
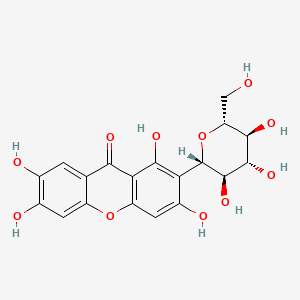
Magniferin, 1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone-C2-β-d glucoside is a poyphenolic secondary metabolite from class xanthone of Gentianaceae family, potential ability to pave way for modification of other drugs following Lipinki's rule . It comprises of two rings, the ring A is acetate derived and ring B is shikimate derived. It has a presence of solid yellow crystalline with poor solubility, thus, limiting its usage as a potential therapeutic in clinical use.
|