| ImmunCR Id : | ICR1 |
| Chemical Name : | Curcumin |
| Plant Source : | Curcuma longa |
| Nutraceutical information : | Edible, High fractions in turmeric, used as a dieatry supplement |
| Mode of administration : | Oral |
| Immunomodulatory mechanism : | In Vitro Curcumin has been shown to inhibit inflammatory responses by suppressing COX-2 and NO, NF-ĸB, iNOS, and lipoxygenase in IFN-γ or TNF-α–activated macrophages and NK cells. A study by Jain et al. revealed that curcumin significantly reduced the production of IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, and MCP-1 from high glucose-cultured monocytes. In vivo studies to determine the immunomodulatory effects of curcumin were carried out using several animal models. Curcumin reduced the levels of IL6, TNFα, and MCP1 in streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes rats. Moreover, curcumin prevented pancreatic leukocytes infiltration that might initiate ß-cell destruction. In addition, curcumin reduced CD4+ T cell proliferation and IFN-γ release from M-stimulated BDC2·5-splenocytes as well as reduced LPS/IFN-γ–induced dendritic cell maturation. Antigen-specific T-lymphocyte proliferation has also been reduced by curcumin action on both T cells and antigen-presenting cells (APCs) |
| Description : | The chemical compound curcumin, also called diferuloyl methane, is symmetrical. Curcuminoids, a combination of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin, make up the 3-6% polyphenolic chemicals, or curcuminoids, that are present in turmeric. |
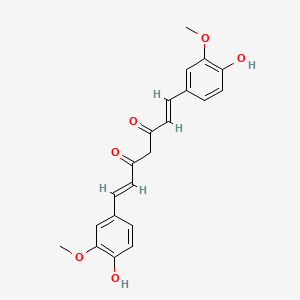
| IUPAC Name | (1E,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione |
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C=CC(=O)CC(=O)C=CC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)OC)O |
| Formula | C21H20O6 |
| InchiKey | VFLDPWHFBUODDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
| Superclass | Phenylpropanoids and polyketides |
| Class | Diarylheptanoids |
| Subclass | Linear diarylheptanoids |
| LogP | 3.554 |
| Molecular weight | 368.38 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor | 2 |
| Polar surface area | 94.092 |
| No. of rotatable bonds | 8 |
| Number of Aromatic Rings | 2 |
| Number of rings | 2 |
| Absorption level | Good |
| Solubility level | Very Soluble |
| Blood Brain Barrier | Low |
| Plasma protein binding | Binder |
| CYP2D6 inhibition | Non-Inhibitor |