Stereochemistry is important to drug activity because the form of a drug molecule influences how it interacts with the numerous biological molecules (enzymes, receptors, etc.). The stereochemistry of the most common phytochemicals is explained here.
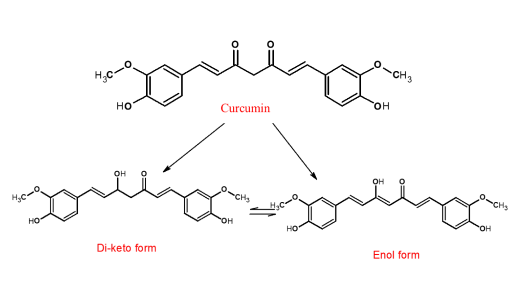
Structure of Curcumin
Biological activity
Metabolism of curcumin
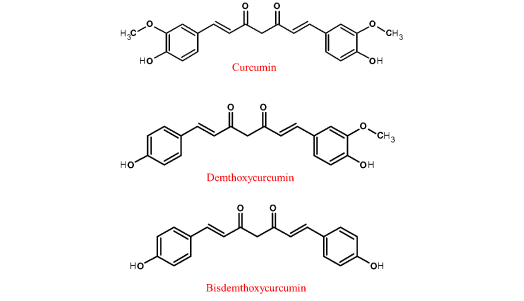
Derivatives of Curcumin
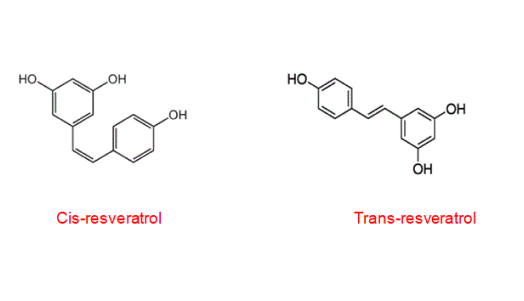
The stilbene-based structure of resveratrol includes two phenolic rings connected by a styrene double bond, allowing it to create 3,4',5-trihydroxystiblene in both cis and trans orientations. Resveratrol exists in both cis and trans forms and trans is the more stable form. Cis trans has antiplatelet and trans has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activity.